Products Details
Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity : Payment Terms : Cash Advance (CA)
- Supply Ability : Ready Per Month
- Delivery Time : Week
- Sample Available : Yes
- Sample Policy : Free samples are available
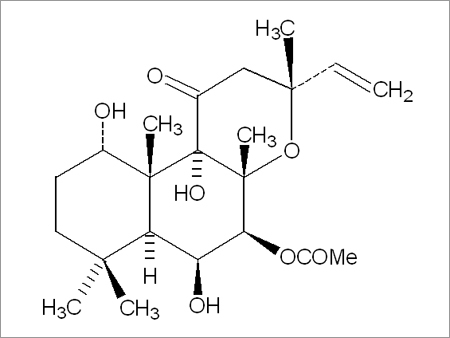
Forskolin
Chemical name : 3R, 4aR, 5S, 6S, 6aS, 10S, 10aR, 10bS, 5 Acetoxy, 3 ethenyldodecahydro 6, 10, 10b, trihydroxy 3, 4a, 7, 7, 10a- pentamethyl- 1H- naphtho [2,1- b] pyran-1- one.
Common names : Coleonol, colforsin, boforsin.
Molecular formula : C22H37O7
Molecular weight : 410.50
Description:
White to off-white crystalline powder, slightly bitter in taste.
Solubility : Soluble in alcohol, chloroform, benzene. Insoluble in petroleum ether, hexane, water.
Physical constant : MP 230-2320C. Optical rotation []: -26.190° (c = 1.68 in Chloroform) Absorption max. – 210, 305 nm
Assay : Purity min. 98%
Uses:
Vasodilating, Cardiostimulatory, hypotensive activity, inhibits aggregation of human splatelets, acts as brochodilator and decreases intraoccular pressure; thus, indicated in conditions like hypertension, congestive heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases, asthma, glaucoma, eczema, and psoriasis4. Adenylate cyclase activating properties, used as leaning agent in obesity. Also in purification of Adenylate cyclase1.
Quantitative determination of forskolin:
- High performance liquid chromatography method:
Column : Reverse phase C18e, 5m
Mobile phase : Acetonitrile Water (50:50).
Wavelength : λmax. 220nm
Chemical nature of forskolin:
Forskolin is a naturally occurring phytoconstituent, chemically belonging to the class of labdane diterpenes. It is present in the roots of plant Coleus forskohlii Briq. Belonging to the family Lamiaceae or labiatae2. Forskolin is the last compound to be formed in the biogenetic sequence of the polyoxygenated diterpenes3.
Mechanism of Action:
Forskolin directly activates the adenylate cyclase and raises cyclic AMP levels in a variety of tissues. Cyclic AMP is an important cell-regulating compound. Once formed it activates many other enzymes involved in diverse cellular functions. Under normal situations cAMP is formed when a stimulatory hormone (e.g., epinephrine) binds to a receptor site on the cell membrane and stimulates the activation of adenylate cyclase. This enzyme is incorporated into all cellular membranes and only the specificity of the receptor determines which hormone will activate it in a particular cell. Forskolin appears to bypass this need for direct hormonal activation of adenylate cyclase. As a result of this direct activation of adenylate cyclase, intracellular cAMP levels rise. The physiological and biochemical effects of a raised intracellular cAMP level include: inhibition of platelet activation; inhibition of mast cell degranulation and histamine release; increased force of contraction of heart muscle; relaxation of the arteries and other smooth muscles; increased insulin secretion; and increased thyroid function.
References:
- The Merck index, Merck and Co. Inc.; Susan Budavari; Thirteenth edition; Merck & Co., Inc. pp. 433. (2500).
- Bhat, S. V., Bajwa, B. S., Dornauer, H., De’Souza, N. J. and Fehlhaber, H. W.; Tetrahedron Letters; 1977; 19; 1669-1672.
- Trease and Evans, ‘Pharmacognosy’, 15th Edition, W. B. Saunders publications, pp. 321-322
- The wealth of India, First Supplement Series- Raw Materials. , CSIR, 2001,Vol. 2, 155-156.
- De’Souza, N. J. and Shah V., Economical and Medicinal Plant Research, vol. 2, 1988, 1-16.
